F.No. 11-1/2019-INC:—In exercise of the powers conferred by sub-section (1) of Section 16 of Indian Nursing Council Act, 1947 (XLVIII of 1947) as amended from time to time, the Indian Nursing Council hereby makes the
following regulations namely:—
Short Title and Commencement—
1. These Regulations may be called the Indian Nursing Council {Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery (NPM) Program}, Regulations, 2020
2. These Regulations shall come into force on the date of notification of the same in the Official Gazette of India. Definitions In these Regulations, unless the context otherwise requires,
i. ‘the Council’ means the Indian Nursing Council constituted under the Act;
ii. ‘SNRC’ means the State Nurse and Midwives Registration Council, by whichever name constituted, by the respective State Governments;
iii. ‘RN & RM’ means a Registered Nurse and Registered Midwife (RN & RM) and denotes a nurse who has completed successfully, recognized Bachelor of Nursing (B.Sc. Nursing) or Diploma in General Nursing and Midwifery (GNM) course, as prescribed by the Council and is registered in an SNRC as Registered Nurse and Registered Midwife;
1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
1.1 Introduction
In 2015, India became one of the 193 countries to commit to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which aims to transform the world by 2030 to a more prosperous, more equal, and more secure planet for all. Needless to say, India’s responsibility is immense as these ambitious goals cannot be achieved without accelerating progress in one-sixth of the world that resides in our country. Health is central to commitments made by the Government of India. For us to be able to ensure healthy lives and promote wellbeing for all ages, it is critical to focus on improving our core health indicators, which include maternal and infant mortality. When a pregnant woman enters the health system, she puts her faith in the system to receive high-quality services for herself and her newborn. Responding to this faith India has strengthened maternal and child health services in our country under the National Health Mission. India has made tremendous progress over the last few decades in increasing institutional deliveries through the National Health Mission and schemes like the Janani Suraksha Yojana and Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram, and this has greatly reduced maternal and infant mortality. India’s maternal mortality ratio has declined from 254/lakh live births in 2004-06 to 130/ lakh live births in 2014-16 (Sample Registration System. India has shown impressive gains in the reduction of Maternal Mortality evident from the fact that the compound annual rate of decline of MMR has increased significantly from 5.8% during (2007-09 to 2011-13) to 8.01% (2011-13 to 2014-16). Similar achievements are also visible in the reduction of under-five and infant mortality rates. Investments in maternal and child health remain a key focus area under the National Health Mission. Operationalizing First Referral Units, new Maternal and Child Health Wings, Obstetric High Dependency Units and Intensive Care Units, capacity building initiatives such as Dakshata training, quality antenatal care strengthening programs such as the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matriva Abhiyan, etc continue to be a key priority.
In addition to the above, the Government of India has recently launched the LaQshya- Labor Room and Maternity Operation Theatre Quality Improvement Initiative. Substantial global evidence exists that addressing the time around and immediately after childbirth is critical for saving the lives of mothers and newborns. Studies conducted by the White Ribbon Alliance has also highlighted the need to focus on respectful maternity care. The LaQshya program has thus been launched to provide quality intrapartum and immediate postpartum care and promote respectful maternity care.
Despite the tremendous progress, nearly 32,000 pregnant women each year still lose their lives during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postnatal period each year. In addition, 5,90,000 newborns die every year in the first month of life. Additional efforts are needed in India to increase Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for maternal and newborn and child health. The National Health Policy 2017 aims at the reduction of maternal mortality ration to 100/ lakh live births by 2020. The survival of women and newborns is closely correlated with the care and attention received during pregnancy and, most importantly, at the time of delivery. Delayed management of cases, due to lack of access to skilled care, is one of the major reasons for the deaths, particularly in the rural areas. Skilled and respectful care during childbirth is important because millions of women and newborns develop serious and hard to predict complications before, during, or immediately after delivery. Evidence shows that quality midwifery care, provided by midwives educated to international standards, reduces maternal and newborn mortality and stillbirth rates by 83% and with 56 improved maternal and newborn health outcomes. It is also evident that 87% of services can be delivered by midwives educated to international standards. There also has been an increasing body of evidence globally that Midwife-led Care Units (MLCUs) can address maternal and neonatal mortality and morbidity by promoting quality and continuity of care through the provision of women-centric care and promoting natural births. Where a model of Midwife-Led Continuity of Care (MLCC) is introduced, this reduces preterm birth by 24%. Beyond survival, quality midwifery care improves breastfeeding rates and psychosocial outcomes, and reduces the use of unnecessary interventions, in particular, cesarean sections, and increases access to family planning (Lancet Series, 2014; UNFPA, 2014 & WHO 2017).
The International Confederation of Midwives outlines the Midwifery philosophy and model of care1. Midwifery has a unique body of knowledge, skills, and professional attitudes drawn from disciplines shared by other health professions such as science and sociology but practiced by midwives within a professional framework of autonomy, partnership, ethics, and accountability. Midwifery is an approach to the care of women and they’re newborn infants whereby midwives: optimize the normal biological, psychological, social, and cultural processes of childbirth and early life of the newborn; work in partnership with women, respecting the individual circumstances and views of each woman; promote women’ s personal capabilities to care for themselves and their families; collaborate with midwives and other health professionals as necessary to provide holistic care that meets each woman’s individual needs. Midwifery care is provided by an autonomous midwife.
1.2 The ‘ Midwifery Services Initiative’ of India
Considering the need for trained human resources to provide quality care to 30 million pregnancies every year in India and at the same time recognizing the challenges earlier, the Government of India has proposed an alternative model of service provision for strengthening reproductive, maternal, and neonatal health services by nurse practitioners in midwifery through Midwife Led Care Units (MLCUs). Quality maternity care provided by midwives through the Marcus is vital to this transformation. The recognition that quality of care will not only save lives but will also provide a positive experience of childbirth means that the change required must be transformative. This will require making fundamental changes to the way services are delivered, and the culture of care provided to women. The ‘ Guidelines on Midwifery Services in India’ set transformative change must be at the heart of midwifery education. The ‘Midwifery Services Initiative’ aims to create a new cadre of midwives titled “Nurse Practitioners in Midwifery” (NPM) who are skilled in accordance with ICM competencies, knowledgeable and capable of providing compassionate women-centered, reproductive, maternal, and newborn health services (RMNCH) and to develop an enabling environment for integration of this cadre into the public health system in order to achieve the SDGs for maternal and newborn health (MoHFW, 2018).
1.3 Preparing Nurse Practitioners in Midwifery (NPM) for the future of India
Quality education is essential to prepare international-standard midwives complying with the ICM competencies with the knowledge and skills to provide the full scope of midwifery care that women and newborns need. Evidence indicates that the optimum duration of training required to acquire needed midwifery skills and competencies in 18 months. The existing one year Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery post basic diploma program of the Council is re-designed and upgraded to an 18-month intensive residency program to develop more NPMs for providing respectful, highest standards of quality and evidence-based care at the institution and community levels with specific emphasis on providing safe and competent midwifery care. The essential components for quality midwifery based on the Quality Maternal and Newborn Care (QMNC) framework are integrated into the curriculum.
Philosophy And Model Of Midwifery Care
The Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery (NPM) will be responsible for the promotion of the health of women throughout their life cycle, with a special focus on women during their childbearing years and their newborns. She will be responsible for providing respectful maternity care during preconception, pregnancy, childbirth, and post-natal period including the care of newborns. She will be responsible and accountable for her practice. The NPMs will practice independently and collaboratively with the doctors in the hospital and within the existing peripheral health system consisting of skilled birth attendants, auxiliary nurse midwives, nurses, doctors, and specialists. She can be posted in a facility where no obstetricians are available and provide midwifery care based on predetermined midwifery care protocols alongside treatment protocols and drugs permitted for use by NPMs. Responding to this urgent need, the NPM curriculum is designed in line with ICM competencies for midwives that emphasize humanizing transformation. The curriculum aims to strengthen the technical knowledge, clinical skills, and attitude of the NPMs in midwifery. The training aims to prepare competent NPMs, who can provide quality and compassionate care to the mother, neonate, and family, demonstrating international standards of midwifery practice. The program will also equip the NPMs to utilize the principles of effective communication, counseling, leadership, supervision, and management and enable them to understand and utilize the research end evidence relevant to midwifery practice.
2. PHILOSOPHY AND VISION
2.1 Philosophy
The Council believes that strengthening midwifery education to International Standards is a key step to improving the quality of women-centered respectful care and reducing maternal and newborn mortality and morbidity. The Council believes that registered nurses need to be given additional training to work as a nurse practitioner in midwifery in clinical and community settings to provide Midwifery Led Continuum of Care (MLCC) bringing about transformation in terms of humanization and autonomous role in the midwifery services provided by the NPMs as per the aspirations of the Government of India (GoI). The Council believes that competency-based training integrating ICM competencies would enable the Nurse Practitioners in Midwifery (NPM) to demonstrate knowledge, skills, and behaviors based on sound evidence-based knowledge, focusing on the concept of ‘ women-centered and respectful care’ that is central to midwifery practice. The NPMs will be able to combine their knowledge, skills with interpersonal, social, and cultural competencies and work as part of an inter-professional team. The philosophy of midwifery training is underpinned by the internationally accepted definitions of a midwife, incorporating the globally understood key elements of midwifery care. The ICM defines a midwife as ‘a person who has successfully completed a midwifery education program that is duly recognized in the country where it is located and that is based on the ICM Essential Competencies for Basic Midwifery Practice and the framework of the ICM Global Standards for Midwifery Education; who has acquired the requisite qualifications to be registered and/or legally licensed to practice midwifery and use the title ‘ midwife’ and who demonstrates competency in the practice of midwifery’. This philosophy is adopted by the Council’s philosophy in preparing NPMs through the proposed curriculum.
The Council also believes that a variety of innovative educational strategies can be used in theoretical and clinical settings to provide the best theoretical and clinical learning experiences. The teaching-learning approaches will integrate adult learning principles, competency-based education, collaborative learning, experiential learning, mastery learning, and self-directed learning. The Council also believes that effective collaborative and interdisciplinary learning can be facilitated by involving medical and other faculty from related disciplines such as Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics, and Public Health. It is hoped to facilitate developing policies towards the creation of cadre positions for appropriate placement of these NPMs to function in midwife lead care units (MLCUs) with appropriate career progression opportunities.
2.2 VISION
The program is envisioned to provide high-quality education, which meets international standards and prepares NPMs to work autonomously to their full scope of practice in respectful partnerships with women and in collaboration with the obstetrician, pediatrician, and the other health care team members when indicated, to provide compassion, quality, evidence-based, woman-centered, and family-focused care during pregnancy, labor, and postnatal period. The program prepares NPMs to champion positive childbirth experience, the optimal transition to parenthood, and safe reproductive health care. The nurse practitioners in midwifery from this program will meet the educational and practice standards of the Council with a focus on the ICM Essential Competencies for Midwifery Practice. They will uphold recognized standards of midwifery practice, embrace, support the qualities and values of the midwifery practice, and be motivated, flexible, and evidence-informed practitioners. They will be prepared to grow and advance through learning and continuing experience. The NPMs are equipped to work within midwifery-led care and continuity of care models in India, both within the newly formed midwife-led care units within public health facilities and/or integrated into primary health care within the community.
3. AIM & OBJECTIVES
3.1 AIM
The aim of the Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery program is to prepare a cadre of NPMs who are confident and skilled in accordance with competencies prescribed by the ICM and the Council for providing high quality respectful, dignified, compassionate, and evidence-based midwifery care to woman, newborn, and family and working autonomously with their full scope of practice, as per regulations of the Council/MoH& FW.
3.2 OBJECTIVES
The program will prepare the NPMs to
3.2.1 Facilitate a positive childbirth experience for women and their families, placing women at the center of care inclusive of psychosocial, spiritual, and cultural background across community settings and within institutions contributing to natural childbirth providing humanized care to improve the quality of care
3.2.2 Work in partnership with women, families, and the other health care team to plan and provide the necessary support, care, and advice during pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period up to six weeks
3.2.3 Advocate for ethical, compassionate respectful, and culturally sensitive care in pregnancy, labor, and childbirth, and post-partum, including promoting the woman’s autonomy and rights to informed decision making
3.2.4 Contribute to the reduction of over-medicalization of maternity care and reduce impacts of socioeconomic inequalities including hard to reach and tribal areas
3.2.5 Educate women individually or in groups to have knowledge about family planning, a healthier pregnancy including diet, nutrition, mother-baby bonding, breastfeeding support, family integrity, and optimal start to life to enhance health and disease prevention
3.2.6 To assume responsibility for her own decisions and actions as an autonomous primary maternity care practitioner and lifelong learner
3.2.7 Recognize abnormalities and complications and implement appropriate management and care, including managing emergency care and timely referral
3.2.8 Draw on research-informed/evidence-based knowledge to be an effective problem solver and to think critically and reflect on practice
3.2.9 Work within the legal and professional boundaries by understanding their role within the broader health care profession and engage inter-professionally; with doctors, nurses, and other health care providers as part of a maternity care team
4. CURRICULUM- CONCEPTUAL MODEL
Midwifery Education recognizes that learning and continuing competency are lifelong pursuits thus this the curriculum aims to facilitate a passion for learning through well-designed teaching and learning strategies aligned to evidence-informed and contemporary midwifery knowledge and practice. The conceptual model has been designed to reflect a holistic approach to midwifery education. Conceptually, it sets seven core values at the center of the curriculum, highlighting qualities that are central to provide a positive childbirth experience. Key approaches that inform contemporary midwifery practice are integrated throughout the curriculum, alongside maternity and newborn care priorities. The ICM Essential Competencies for Midwifery Practice and the Council educational and practice standards direct the course aims, objectives, and content. The course delivery will incorporate evidence-informed teaching and learning principles. The values, integrated concepts, maternity care priorities, midwifery competencies, teaching and learning principles are informed by the Guidelines on Midwifery Services in India, Strengthening Quality Midwifery Education Framework for Action, The Framework for Quality Maternal and Newborn Care, and Lancet Series on Midwifery, Council’s Educational and practice standards, ICM Essential Competencies for Midwifery Practice and ICM Global Standards for Midwifery Education. The curriculum conceptual model that informs the overall program design and course development is illustrated in Figure 1 below.
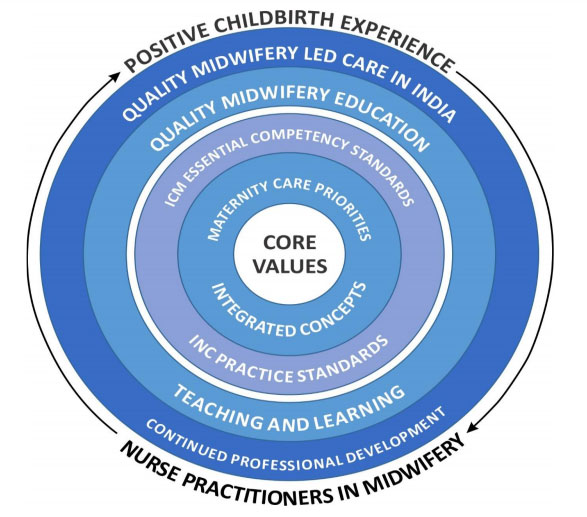
4.1 Curriculum Principles
4.1.1 Core values
The core values provide a foundation to develop midwives who are committed to promoting a positive childbirth experience for all women and were derived from core government, WHO, and ICM documents. These values include;
(i) compassion
(ii) respect
(iii) woman, baby, and family-centredness
(iv) equity and rights
(v) collaboration and teamwork
(vi) ethical practice,
(vii) moral courage.
4.1.2 Integrated concepts
Within the curriculum, there are seven concepts that represent key approaches that inform contemporary midwifery practice. These concepts include:
(i) social inequities and midwives as primary health practitioners
(ii) evidence-based midwifery practice (iii) cultural competence
(iv) quality maternity and newborn care
(v) continuity of midwifery care
(vi) midwifery as a relationship between a woman, baby, family, and a midwife
(vii) optimizing physiological birth (viii) Community knowledge.
4.1.3 Maternity care priorities
The program provides a strong focus on identified maternity care needs and priorities which are addressed across the curriculum
(i) improving maternity and newborn care for vulnerable and hard to reach women,
(ii) reducing maternal and newborn maternity and morbidity
(iii) effective management of emergency care
(iv) Human rights and gender-based violence
(v) strengthening midwifery-led care
(vi) humanizing and promoting natural childbirth
4.1.4 ICM Essential competency standards for midwifery practice and Council’s practice standards
The ICM (2019) competencies are grouped under four main categories. They are
- General competencies that apply to all aspects of midwifery practice and specific competencies that are specific to
- Pre-pregnancy and antenatal
- Labour and birth
- Ongoing care of a woman and newborn. These competencies provide a framework for the courses within the program. The Council practice standards guide midwifery practice and provide regulations.
4.1.5 Continued Professional Development
The quality of midwifery practice is achieved when the practice is led by the autonomous role of NPMs. Continued professional development is essential for advancing and building the future of midwifery practice in India
5. SCOPE OF PRACTICE
- The NPM is recognized as a responsible and accountable professional who works in partnership with women to give the necessary support, care, and advice during pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period, to conduct births on the midwife’s own responsibility, and to provide care for the newborn and the infant.
- This care includes preventative measures, the promotion of normal birth, the detection of complications in mother and child, the accessing of medical care or other appropriate assistance, and the carrying out of emergency measures.
- The NPM/midwife has an important task in health counseling and education, not only for the woman but also within the family and the community. This work should involve antenatal education and preparation for parenthood and may extend to women’s health, sexual or reproductive health, and childcare.
- NPM may practice autonomously in any setting including the home, community, hospitals, clinics, or health units mostly in MLCUs that is envisaged by GoI.
- The NPM will be able to perform the full scope of practice as per education and training and Council’ s/MoHFW regulations and guidelines.
6. COMPETENCIES
The Council adopted the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) competencies for the training of nurse practitioners in midwifery for India and the framework is given below:
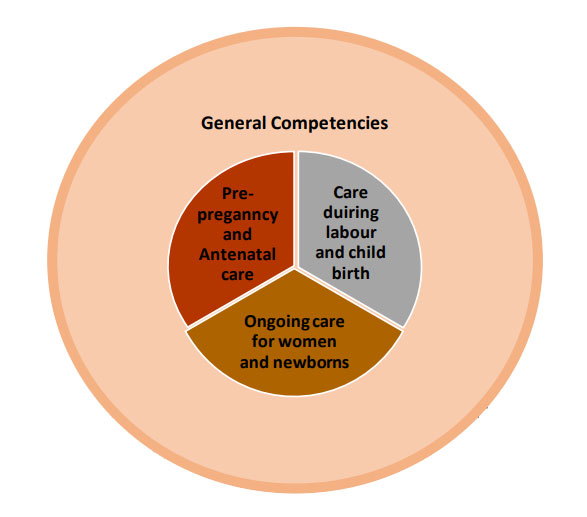
COMPETENCY CATEGORY 1: GENERAL COMPETENCIES
NPMs demonstrate professional accountability as an autonomous practitioner in the delivery of midwifery care as per ICM standards adopted by the Council that is consistent with moral, altruistic, and humanistic principles in midwifery practice.
Competencies:
1a. Assume responsibility for own decisions and actions as an autonomous practitioner
1b. Assume responsibility for self-care including personal safety and self-development as a midwife
1c. Appropriately delegate aspects of care and provide supervision
1d. Utilize research to inform practice
1e. Uphold the fundamental human rights of individuals when providing midwifery care
1f. Adhere to jurisdictional laws ethical, regulatory requirements, codes of conduct for midwifery practice
1g. Facilitate women to make individual choices about care
1h. Demonstrate effective interpersonal communication with women and families, health care teams, and community groups
1i. Facilitate normal birth processes in institutional and community settings, including women’s homes
1j. Assess the health status, screen for health risks, and promote general health and well-being of women and infants
1k. Prevent and treat common health problems related to reproduction and early life
1l. Recognize conditions outside midwifery scope of practice and refer appropriately
1m. Care for women who experience physical and sexual violence and abuse
COMPETENCY CATEGORY 2: PRE-PREGNANCY AND ANTENATAL CARE
NPMs Perform health assessment of woman and fetus, promote their health and well-being, detect complications during pregnancy, and provide care to women with an unexpected pregnancy
Competencies:
2a. Provide pre-pregnancy and antenatal care
2b. Determine the health status of women
2c. Assess the fetal wellbeing
2d. Monitor the progression of pregnancy
2e. Promote and support healthy behaviors that improve their wellbeing
2f. Provide anticipatory guidance related to pregnancy, birth, breastfeeding, parenthood, and change in the family
2g. Detect, manage, and refer women with complicated pregnancies
2h. Assist the woman and her family to plan for an appropriate place of birth
2i. Provide care to women with an unintended or mistimed pregnancy
COMPETENCY CATEGORY 3: CARE DURING LABOUR AND CHILDBIRTH
The NPMs continue to monitor and provide care to women during labor that facilitates physiological processes and safe birth, immediate care to newborn infants,s and detection complications in mother and infant.
Competencies:
3a. Promote physiologic labor and birth
3b. Manage a safe spontaneous vaginal birth and prevent complications
3c. Provide care of the newborn immediately after birth
COMPETENCY CATEGORY 4: ONGOING CARE OF WOMEN AND NEWBORNS
The NPMs continue to perform health assessments of mother and infant, provide health education and support for breastfeeding, detect complications, and initiate family planning services.
Competencies:
4a. Provide postnatal care for the healthy woman
4b. Provide care to a healthy newborn infant
4c. Promote and support breastfeeding
4d. Detect and treat or refer to postnatal complications in a woman
4e. Detect and manage health problems in the newborn infant
4f. Provide family planning services
7. PROGRAM DETAILS
7.1 PROGRAM DESCRIPTION
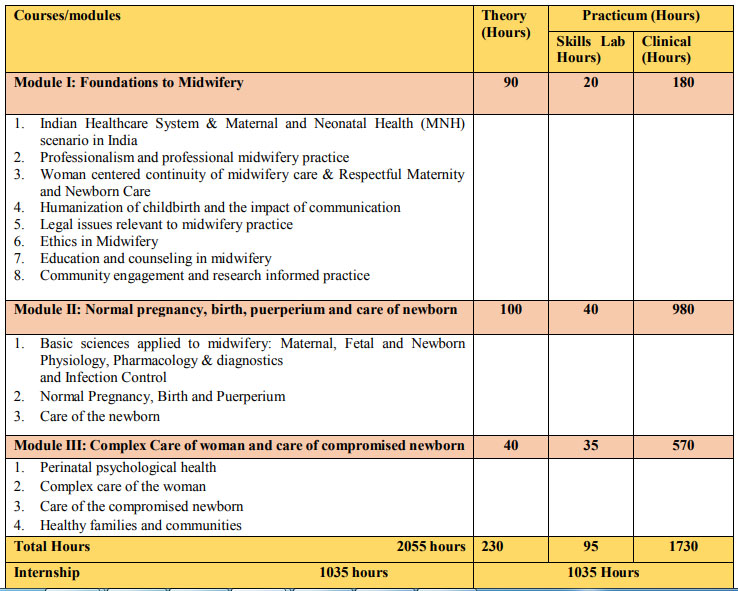
The NPM program is an 18-month residency program, which includes 12 months of residency education and training followed by 6 months of intensive practicum/internship. The program mainly focuses on Competency-based education and training facilitated by mastery and experiential learning centered around transformational and relationship-based teaching and learning integrating Council’s/global educational and midwifery practice standards. The change in a paradigm shift to women-centered and respectful midwife-led midwifery services is emphasized throughout the program recognizing their scope of practice. The curriculum comprises of theory and practicum (lab and clinical), offered in four-course modules namely
i) Foundations to midwifery
ii) Normal Pregnancy, birth, postpartum, and care of newborn
iii) Complex care of woman and care of compromised newborn. Besides the foundational training, the curriculum encompasses hands-on skill training and orientation to the treatment protocols/national midwifery guidelines and drugs permitted for use by NPMs relevant to midwifery practice
The program is designed so that learning is scaffolded across the program to enable the progressive development of the knowledge, skills, and values essential for the students to practice with professional competence as qualified midwives recognizing that the students are registered nurses with some prior midwifery experience. The first two series of courses provide the opportunity to develop contemporary midwifery knowledge, skills, and values with a focus on promoting normal pregnancy, birth, and puerperium, including healthy fetal and neonatal development. The third set of courses focuses on the deviation from normal including complex care of the woman and newborn as well as the midwife’s role in primary health care. The final four courses focus on readying the student for their role as an autonomous midwife practitioner working in and advocating the new model of midwifery-led care in India. As described in the curriculum conceptual model, students have the opportunity for consolidated learning. The integrated concepts are incorporated into content and learning activities that increase in complexity throughout the program. Alongside this, maternity care priorities are addressed with varying emphasis depending on course objectives. Similarly, the core values and ICM Essential Competencies are also interwoven into course content, learning activities, and practice experience throughout the program.
7.2 PROGRAM STRUCTURE
7.3 GUIDELINES FOR STARTING THE NURSE PRACTITIONER MIDWIFERY PROGRAM
7.3.1 The program may be offered at
- The Government (State/Center/Autonomous) nursing teaching institution offering degree programs in nursing having parent / affiliated Government Hospital facilities of maternity, and neonatal units along with primary, secondary, and tertiary health care facilities.
Or
- Other Non-Govt. nursing teaching institution offering degree programs in nursing having parent hospital facilities of maternity and neonatal units along with primary, secondary, and tertiary health care facilities.
- The eligible institution shall get recognition from the concerned SNRC for starting the Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery program for the particular academic year, which is a mandatory requirement.
- The Council will conduct an inspection for two consecutive years for the continuation of the permission to conduct the program.
7.3. 2 Staffing
- NMP Faculty: M.Sc. Nursing with OBG/Pediatrics/Community health nursing specialty or B.Sc. (N) with NPM educator training
- Medical Preceptors: Medical faculty from Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics and Public Health with 3 years post PG experience/ consultant
- Guest faculty: NHM/MoH&FW officials/Experts from other fields
Teacher-student ratio– 1:10
Preceptor student ratio-1:10
No. of seats –Maximum 30 per batch
7.3.3 Physical facilities
- Classroom – 1
- Skills/simulation lab– 1 with necessary equipment and supplies
- Library – Current nursing textbooks including midwifery, maternal, neonatal and
journal (National and International publications), relevant GOI guidelines/modules - Teaching Aids –
:: LCD projector
:: Screen for projection
:: Computer
:: Laptop
:: Tablet for IT applications (Forex. Safe Delivery App, e-Partograph, and other apps)
:: Connectors to project tab screens to an external screen
:: 4 Mbps internet leased line - Office facilities for midwifery educators
7.3.4 Clinical facilities
Minimum Bed strength and other Clinical Facilities:
100-200 bedded Parent Hospital having minimum 50 maternity beds or 50 bedded maternity hospital with an established MLCU
- Labor room as per the LaQshya guidelines of Government of India
- Minimum 6 labor tables/beds
- Maternal and neonatal units
- The caseload of a minimum of 6000 deliveries per year
- Maternity OT and Obstetric HDU/ICU
- Separate Kangaroo Mother Care Unit
- 8-10 level II neonatal beds
- Affiliated Heath Subcentre, Community Health Centre, and Primary Health Centre
- Referral links to tertiary care hospital
- Affiliation to Tertiary Hospital – Medical College Hospital
- Affiliation with level III neonatal beds
7.4. ADMISSION REQUIREMENTS
7.4.1 Eligibility for admission
The candidate seeking admission to this program should have the following qualifications:
- Registration Be an R.N. and
R.M. with Diploma in General Nursing and Midwifery or BSc. (N) qualification - Possess a minimum of two years of recent clinical experience in maternity care with a passion for midwifery.
- In-service candidates are also eligible for admission and will be receiving their regular salary. Being a residency program, the other students undergoing the program will be given salary equivalent to their counterparts in the respective organization.
- Age 45 years or younger at the time of admission
- Registration Be an R.N. and
Note: The candidate in order to practice midwifery during the period of training, has to obtain temporary/transfer
registration (R.N and
R.M) in the respective state where the candidate is enrolled in the NPM program.
7.4.2 Selection process
Selection Criteria and Process Overview for Recruitment of NPM is outlined below:
The Entrance exam will be conducted in two parts with a certain percentage of weightage for each component. The overall score for the entrance examination is 100 marks (60 for written test and OSCE and 40 for interview).
- Part 1 -Written test and OSCE:
– Written Test (40%): Multiple Choice Questions and two short essays (2 hours duration) covering the areas of antenatal, intrapartum, postnatal, complication management, and neonatal care. Short essays will be screened for technical proficiency as well as fluency in written English. Some weightage should be given for proficiency in written English.
– OSCE- Objectively Structured Clinical Examination (20%) - Part 2-Interview (40%)
Successful candidates who clear the written test and OSCE will be screened for the following at the interview:
1) Motivational Screening (20%) Based on the information provided in the personal statement of the candidate:
a) Passion for woman’s health-to provide respectful care for a positive birthing experience.
b) Willingness to undergo the 18-month residential course at the designated SMTI
c) Willingness to serve as individual practitioners of midwifery care-low-risk pregnancies and normal births as posted after the training
2) Aptitude assessment (20%) will be a part of the interview process to ascertain spoken the English language
proficiency an
- Part 1 -Written test and OSCE:
7.5. ORGANIZATION OF THE PROGRAM
7.5.1 Distribution of the program in weeks (78 weeks):
First 12 months: 52 weeks
- Annual Leave + Casual Leave + Sick Leave + Public holidays = 4weeks
- Exam preparation and examination = 2weeks
- Theory and practicum (skill lab and Clinical) = 46 weeks
Second six months: 26 weeks of internship
- Annual Leave + Casual Leave + Sick Leave + Public holidays = 2weeks
- Exam (competency assessment) = 1week
- Internship experience = 23weeks
7.5.2 Implementation of the curriculum
First 12 months (46 weeks)
Block classes- 3wks x 40hrs = 120hrs
Clinical Residency of 43 weeks x 45hrs/week = 1935 hrs
Total: 2055 hours
7.5.3 Distribution of the Courses for teaching (52 weeks = 2055 hrs)
DETAILS |
| Block classes 3 weeks x 40hrs /week = 120 hours (Full theory block classes: Theory 90 hrs + skill lab 30 hrs) |
| Clinical residency 43weeks x 45 hrs / week = 1935 hrs (Theory-140 hours + Skills lab-65 hours + Clinical-1730 hours)
|
Total=230 Hrs (theory)+95Hrs(skills lab)+1730Hrs (clinical practice) = 2055 hrs |
7.6. COURSE OF INSTRUCTION
S. No | Courses/Modules | Theory | Practicum (Skill Lab (SL) + Clinical Lab( CL)) | Areas of Clinical Postings |
I | Module I: Foundations to Midwifery | 90 | 20 SL +180 CL | Integrated clinical practice at All maternity areas of the hospital/ |
1 | Indian Healthcare system & Maternal and Neonatal Health (MNH) scenario | 10 | 20 CL | |
2 | Professionalism and professional midwifery practice | 18 | ||
3 | Woman centered continuity of midwifery care & Respectful Maternity and Newborn Care | 6 | 8 SL+40 CL | |
4 | Humanization of childbirth and the impact of communication | 10 | 8 SL+ 20 CL | |
5 | Legal issues relevant to midwifery practice | 6 | ||
6 | Ethics in Midwifery | 4 | Integrated clinical practice at All maternity areas of the hospital/ | |
7 | Education and counseling in midwifery | 6 | 2 SL+ 20 CL | |
8 | Community engagement and Research Community responsibility & leadership and Research-informed practice | 30 | 2 SL+80 CL | |
II | Module II: Normal pregnancy, birth, puerperium, and care of newborn | 100 | 40 SL+ 980 CL | |
1 | Basic sciences applied to midwifery: Maternal, Fetal and Newborn Physiology, Pharmacology & diagnostics and Infection Control | 40 | 12 SL+210 CL | Integrated clinical practice |
2 | Normal Pregnancy, Birth and Puerperium | 50 | 22 SL+ 680 CL | Antenatal OPD/ ward Labour room / casualty Postnatal ward / OPD |
3 | Care of the newborn | 10 | 6 SL+90 CL | SNCU/NICU / postnatal ward |
III | Module III: Complex Care of woman and care of compromised newborn | 40 | 35 SL+570 CL | |
1 | Perinatal psychological health | 4 | 60 CL | ANC Ward/Labour Room/ PNC ward |
2 | Complex care of the woman | 25 | 20 SL + 330 CL | Antenatal OPD / ward/Obstetric HDU/ICU Labour room / casualty/maternity OT/Obstetric HDU/ICU Postnatal ward / OPD/ Obstetric HDU/ICU |
3 | Care of the compromised newborn | 8 | 10 SL + 130 CL | NICU / Postnatal ward / OPD |
4 | Healthy families and communities | 3 | 5 SL+ 50 CL | ANC OPD/Postnatal OPD / ward / FP ward |
Total =2055 hours | 230 hours | 95 SL+ 1730 CL hours |
7.7. CLINICAL PRACTICE
7.7.1 Clinical Residency experience
(A minimum of 45 hrs/ week is prescribed, however, it is flexible with different shifts and OFF followed by on-call duty every week or fortnight)
7.7.2 Clinical postings
The students will be posted to the under mentioned clinical area during their training period
First 12 months S/No | Clinical area | Week/s |
1 | Antenatal (AN) OPD | 6 |
2 | Antenatal (AN) Ward | 4 |
3 | Labour Room | 12 |
4 | Postnatal (PN) Ward & OPD | 4+1 |
5 | NICU (SNCU) | 2 |
6 | OBS Casualty | 1 |
7 | OBS OT | 1 |
8 | OBS ICU | 2 |
9 | Family planning ward | 1 |
10 | PHC/CHC | 4 |
11 | MLCU | 4 |
| TOTAL | 42 |
Next 6 months of Internship
S/No | Clinical area | Week/s |
1 | AN OPD & Ward | 3 |
2 | PN OPD & Ward | 3 |
3 | Labour Room | 6 |
4 | NICU(SNCU) | 2 |
5 | OBS Casualty & ICU | 3 |
6 | OBS OT | 1 |
7 | PHC/CHC | 3 |
8 | Miscellaneous | 1 |
| TOTAL | 22 |
8. TEACHING AND LEARNING
Teaching-learning within the NPM curriculum draws on Experiential Learning theories. Experiential learning recognizes that learning is an active process that occurs as students interact with authentic activities, experiences, and social encounters. The educational process is underpinned by respect, with educators modeling the respectful care and communication that these graduates will engage in with women. The student is intentionally situated at the center of learning and becomes directly involved in the process of constructing knowledge. As such, experiential learning relies on experience, as the source material and thoughtful reflection to facilitate learning. Providing ‘real world’ context to activities and experiences aligns students learning to the types of practice and complexities they might encounter as midwifery graduates. Motivation and engagement increase as students work with real-life situations that require decision-making that reflect the nature of maternity care environments and promote autonomous roles that need to be assumed upon completion of the program and called to lead midwifery care in MLCUs.
Experiential learning is also committed to minimizing the theory-practice gap that has been recognized as a challenge in contemporary tertiary health care education. Experiential learning integrates practice with theory, avoiding teaching and learning which occurs in silos. As part of the experiential learning pedagogy, students will engage in significant practice experience through midwifery practicums. Practicums will be organized to reflect a diversity of clinical settings across the continuum of pre-conception, childbirth, to postpartum and will include hospital and community settings. Students will also be required to engage in defined continuity of care experiences where they follow women through their pregnancy, labor, birth, and puerperium.
Complementing Experiential Learning in this program is Scenario-Based Learning (SBL) and reflective practice. SBL uses scenarios that reflect realistic situations, for example, they may be based on case studies, critical incidents, or narratives, which provide contextual material and/or learning triggers and provide an ideal environment for exploring practice, complexities and encourage critical thinking, problem-solving and decision-making skills. The learning processes in SBL move through phases that require students to engage in the scenario, analyze the situation, identify learning needs, construct knowledge, reflect, and apply to learn. Scenario-based learning is best provided through tutorials and flipped classrooms, where students can access pre-tutorial readings and recorded lectures to support the interactive nature of the learning.
A dedicated simulated environment will be developed to provide a safe learning environment where students will have the opportunity through simulation workshops to develop midwifery skills, work in teams, explore scenarios and problems, and practice clinical decision-making. Carefully designed simulation activities will also provide the opportunity to develop communication skills relevant to the women’s needs and health problems, including interacting with scenarios representing families from different demographic and cultural backgrounds, which is vital considering India’s cultural and demographic diversity. Inter-professional learning may also be fostered through implementing team simulation scenarios
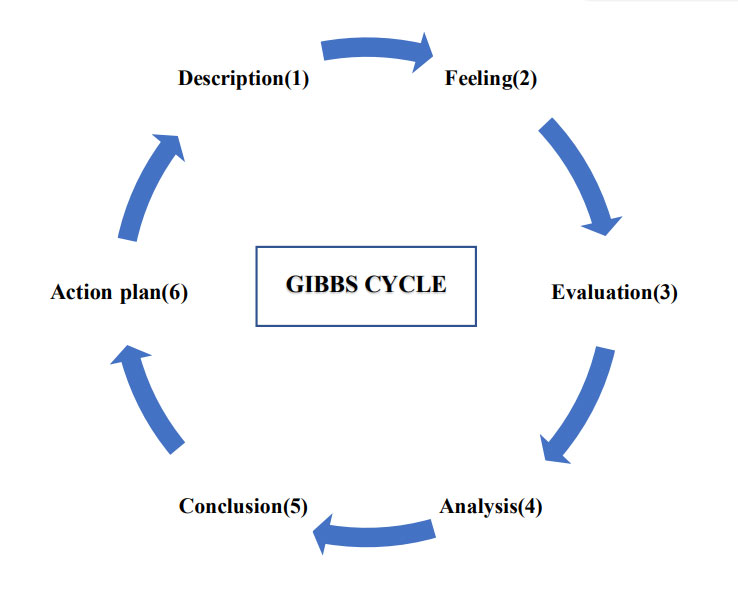
The reflective practice assists students to learn from experience, both positive and negative, and to gain new insights about themselves and practice. Gibbs cyclic model provides a six-stage approach to systematically reflect on an experience or activity; including description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and an action plan.
Experiential learning supported by scenario-based learning and reflective practice will be integrated throughout the curriculum in both theoretical and practice components. Teaching and learning arrangements will be organized to encourage collaboration and interaction, examples of teaching modes include tutorials and group work, online resources and lectures, smart classrooms, personal research and reflection, experiential workshops, journal club, post clinical reviews.
8.1: Teaching and learning methods
Classroom | Skills lab | Clinical |
|
|
|
| Example:* EdTech based learning may be incorporated throughout the curriculum by the integration of the Safe Delivery App into the various teaching methodologies. The Safe Delivery App is a smartphone application that provides direct and instant access to evidence-based and up-to-date clinical guidelines on BEmONC. The SDA is used as a teaching and learning tool that covers 11 modules: (Infection Prevention, Post Abortion Care, Hypertension, Active Management of Third Stage Labour, Prolonged Labour, Postpartum Haemorrhage, Manual Removal of Placenta, Maternal Sepsis, Neonatal Resuscitation, Newborn Management, Low Birth Weight) | ||
8.2: Assessment methods
8.2.1 Continuous Formative Assessments (Internal Assessment)
- Seminar
- Self-assessment through reflective learning as well as peer review
- Written assignments (Case studies, Case presentation, Case report, etc)
- Case study and Clinical presentation
- Group work
- Literature reviews
- Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE)
- Practical assessments-teaching activities (health teaching sessions), simulation
- Written examination/Test papers-MCQs, short answers, and essay type
- Competency Assessment
- Clinical performance/practice evaluation
- Quizzes
- Poster Presentations
- Online learning activities
- Class presentations including case studies
- Debates
- Peer Review
- Continuous assessment.
Midwifery practice experiences and reflection activities will be documented in a practice portfolio compiled over the duration of the program. Feedback will be sought from women and midwives (preceptors) with whom students work.
1. EXAMINATION REGULATIONS
9.1: SCHEME OF EXAMINATION
Course/Paper | Int. Ass. Marks | Ext. Ass. Marks | Total marks | Duration (in hours) |
| A. Theory | ||||
| Paper I (Module 1) | 25 | 75 | 100 | 3 |
| Paper-II (Module 2 & 3) | 25 | 75 | 100 | 3 |
| Theory Total | 50 | 150 | 200 | |
| B. Practical | ||||
| Midwifery | 100 | 100 | 200 | |
| Practical Total | 100 | 100 | 200 | |
Grand Total | 150 | 250 | 400 |
Note: The Theory and practical examination have to be conducted by the respective examination board approved by the Council
9.2 ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION TO EXAMINATION
- The percentage of attendance in theory and practical before appearing for the examination should be 90%.
- A candidate who successfully completes the necessary requirement such as logbook and clinical requirements is eligible and can appear for the final exam.
- However, students should make up 100% of attendance for integrated practice experience and internship in term of hours and activities before awarding the certificate
9.3. SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION
- Failed candidates can appear for the supplementary examination after 6 weeks in the exam failed either theory or practical only.
- Number of attempts – 3
9.4 EXAMINATION PATTERN (Theory and Practical)
| Type of Exam | Internal (formative assessment) | External (summative assessment) |
| Theory | 25 marks (tests, assignments, presentations) | 75 marks (10 marks- MCQ, 30 marks- short answers, 35 marks – essay/scenario) |
| Practical | 100 marks (20 for clinical performance + 20 for clinical assignments + 20 for OSCE+40 for DOP) | 100 marks (40 in OCSE + 60 in Directly observed practical (DOP) |
| For practical examination maximum number of students per day = 10 students | ||
9.4.1 Examiners for Practical examination
A panel of three examiners: NPM educators – 2 (one internal and one external) and medical preceptor – 1(The examiners, as well as the medical preceptor, must be involved in teaching the program and be familiar with the curriculum)
9.4.2 Qualification of examiners
- NPM educator, M.Sc OBG nursing with 5 years of teaching and clinical experience after PG – dual role / M.Sc OBG nursing with 5 years of experience as faculty with a minimum of 2 years midwifery clinical working experience.
- Medical faculty/preceptor from Obstetrics and Gynecology, Pediatrics, and Public Health with 3 years post PG experience/consultant.
10. CERTIFICATION
A. Title – Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery (NPM)
B. A title is awarded upon successful completion of the prescribed study program, which will state that she/he
i. Has completed the prescribed course of Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery program for a period of 18 months
ii. Has completed 90% of the theoretical and 100% of the practical instruction hours before awarding the certificate.
iii. Has passed (70% marks both internal and external together) in the theory and practical examination
C. Certification will be done by the Examination Boards as approved by the Council. The SNRC will register
NPM as an additional qualification
1. COURSE DETAILS/ MODULES
COURSE MODULE I: FOUNDATIONS TO MIDWIFERY
Theory: 90 Hours
Practicum: Skill Lab (SL)-20 Hours |
Clinical (CL)- 180 Hours
Course Aim
This course will enable the students to develop a deep understanding of midwifery as a profession and the role and scope of the midwife in both the local and international context utilizing the principles of professional management, leadership, and research-informed midwifery practice.
Course Description
Students will explore the history of midwifery in India; the Indian health care system, Maternal newborn health (MNH) scenario in India, National Family Health Survey; the legal, regulatory, and ethical frameworks and requirements of midwifery practice, including code of ethics and professional conduct, jurisdictional laws, local policy and guidelines, respectful behavior, human rights, humanizing birth, shared decision making, confidentiality, and privacy. Midwifery models of care; global significance and the professionalism of midwifery along with the ICM essential competencies; professional accountability and transparency; inter-professional collaboration and teams; teaching, supervision and mentoring skills; personal and professional resilience; moral courage; clinical reasoning; self-care; and professional audit are also included. There will be a specific focus on respectful and compassionate communication and cultural competency. It will also include community responsibility and midwifery leadership. This course will also support students to develop lifelong learning skills including evidence-based practice; critical thinking skills, critical appraisal; research translation; reflective practice; documentation, and record-keeping.
Objectives:
- Demonstrate professional accountability for the delivery of midwifery care as per INC standards that is consistent with moral, altruistic, legal, ethical, regulatory, and humanistic principles in midwifery practice.
- Identify the role of midwifery philosophy and practice in transforming maternity care in India and globally
- Describe the importance of RMNC and develop strategies to promote respectful and compassionate care Demonstrate compassionate and effective communication skills for respectful and culturally competent midwifery care
- Apply principles of evidence-based practice, critical thinking, and reflection to support autonomous midwifery practice. Utilize the assessment and evaluation data to critically analyze and enhance midwifery practice
- Explore how the midwife collaborates with the inter-professional health care team and the value of respectful teamwork
- Describe the advocacy role of the midwife for women, families, and communities
- Identify and apply legal and ethical principles and provisions for midwifery practice
- Describe the importance of communication, education, and counseling of women and families to participate effectively in midwifery care
- Understand the role of the midwife as an agent of change for transformative practice
- Analyze and apply principles of effective leadership, team building, negotiation, and conflict resolution skills
- Discuss appropriate management of midwifery resources and equitable access to midwifery care
- Review the ethical principles and methodological approaches to research.
- Utilize research to inform practice
Competencies: (ICM)
- Assume responsibility for own decisions and actions as an autonomous practitioner (1a)
- Assume responsibility for self-care including personal safety and self-development as a midwife (1b)
- Appropriately delegate aspects of care and provide supervision (1c)
- Utilize research to inform practice (1d)
- Uphold the fundamental human rights of individuals when providing midwifery care (1e)
- Adhere to jurisdictional laws ethical, regulatory requirements, codes of conduct for midwifery practice (1f)
- Facilitate women to make individual choices about care (1g)
- Demonstrate effective interpersonal communication with women and families, health care teams, and community groups (1h)
COURSE CONTENT:
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
I | T- 10 CL-20 |
| Indian Healthcare system & MNH Scenario Introduction
Health care delivery system:
|
| Group seminar on Maternity care services by GOI |
|
| exploring the new initiative and guidelines Discuss trends, issues, and complexities in relation to maternity care provision in India | ||||||
| Maternal and newborn health (MNH) scenario in India
|
|
|
| ||
II | T -18 |
| Professionalism and professional midwifery
Inter-professional collaboration and teamwork
|
|
|
|
II | T-18 |
| Professionalism and professional midwifery
Inter-professional collaboration and teamwork
|
|
|
|
|
Reflective practice and Clinical reasoning
Personal and professional resilience; self-care; human rights
Teaching, mentoring, and supervision
|
|
| |||
| ||||||
III | T-6 SL-8 CL-40 |
| Woman centered continuity of midwifery care & Respectful Maternity and Newborn care
Integrating cultural competence
| Self-directed learning | Exercises |
|
IV | T-10 SL-8 CL-20 |
| Humanization of childbirth and the impact of communication
Communication
|
(communication workshop) | Roleplay |
|
V | T-6 |
|
|
| Presentation – ethical and legal issues in midwifery | Assessment of presentation |
VI | T-4 |
|
|
| Assignment on ethical principles in midwifery and its importance | Evaluate understanding of the application of ethical principles to situations encountered in midwifery practice |
VII |
| Education and counseling in midwifery
|
|
| Assessment of prepared education materials | |
VIII | T-30 SL-2 CL80 T-4 |
Identify elements underpinning effective team building and negotiation skills Identify strategies to respond to community needs | Community engagement & research-informed practice A. Community responsibility & leadershipMidwifery leadership
Leadership
|
|
| |
| T-6 CL-40 |
| Management in MLCU
|
| Exercise s/ case studies |
| |
| T-2 |
| B. Research-Informed PracticeIntroduction to research methodologies
|
| Essay/short answers and MCQ | ||
| T-2 |
| Research ethics, bias, and research limitations
|
| Essay/short answers and MCQ | ||
| T-6 CL-40 |
| Quantitative & qualitative research
|
|
| Group presentation on research methodologies | |
| T-4 SL-2 |
| Literature review
|
| Review of literature for a research project | Critical analysis and Literature review | |
| T-4 | Identify the different sources of Data and Evidence for Midwifery Practice |
Data Sources and Evidence for midwifery practice (EBMP)
|
|
|
| |
| T-2 |
|
Research dissemination and knowledge translation
|
Designing posters |
Research symposium | Formative poster and research presentation |
COURSE MODULE II: NORMAL PREGNANCY, BIRTH, PUERPERIUM AND CARE OF NEWBORN
{1. Basic Sciences applied to midwifery, 2. Normal pregnancy, birth and puerperium and 3. Care of newborn}
Theory: 100 Hours
Practicum: Skills Lab-40 Hours | Clinical-980 Hours
Course aim
Drawing on the Council’s philosophy and ICM essential competencies for midwifery practice, the course aims to enhance the Knowledge and skills to promote physiological birth and provide skilled, knowledgeable, respectful and compassionate midwifery care to the woman and newborn in both community and institution. The review of knowledge of basic sciences that include anatomy and physiology of reproduction and fetal development, pharmacology & diagnostics and infection control supports the midwifery practice in facilitation of normal physiological birth.
Course Description
This course module is designed to enable the NPMs to review the principles of related biological and behavioral sciences and midwifery to promote physiological birth and provide respectful quality care that includes anatomy and physiology of male and female reproductive system, conception, menstruation and ovulatory cycle; normal physiological changes that occur in pregnancy, labour, birth and puerperium; fetal growth and development, fetal circulation; normal neonatal physiology; development and pharmacology & diagnostics and infection control.
Antenatal care that includes assessment and screening, antenatal education and empowerment; Intrapartum care that includes 1st, 2nd 3rd and 4th stage of labour, assessment of progress, supporting women in labour and birth, promotion of physiological birth; working with pain with non-pharmacological and pharmacological pain relief, assessment of fetus, assessment of perineal trauma, perineal suturing; active and expectant management of 3rd stage, timely referral; and postnatal care that includes maternal care, transition to parenthood – mother, father and family, promoting attachment, skin to skin, establishing breastfeeding, managing breastfeeding challenges, documentation, reporting, community care are dealt in detail. It will address the knowledge and skills required to develop quality practice skills care for the newborn and promote a healthy transition to life that includes immediate care of the newborn, newborn assessment, essential newborn care; complete physical examination; newborn health needs; nutritional needs of the newborn, skin to skin; breastfeeding; maternal newborn bonding; growth and development of the infant; prophylactic measures; immunisaton; providing evidence based information to parents; consideration of cultural norms; and respectful care to newborn.
Course objectives
- Demonstrate professional accountability for the delivery of midwifery care as per the Council’s standards that are consistent with moral, altruistic, legal and ethical and regulatory and humanistic principles in midwifery practice
- Discuss the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system and conception
- Explain fetal and placental growth and development
- Describe the maternal physiological changes that are associated with pregnancy, labour and birth and puerperium.
- Assess and provide pre pregnancy care including counseling
- Assess and provide care for women in the antenatal, intranatal and postnatal period including conduction of normal deliveries
- Assess and provide care for neonates
- Describe the primary physiological adaptations that the newborn undergoes following birth and the physiological basis of secure bonding and attachment.
- Demonstrate sound knowledge of applied pharmacology and principles of prescribing
- Identify and use medicines appropriately in midwifery, obstetric emergencies and complex situations as per GoI guidelines
- Implement infection control practices in maternal and newborn care facilities
Competencies: (ICM)
- Adhere to jurisdictional laws, regulatory requirements, code of conduct for midwifery practice (1f)
- Provide pre-pregnancy care (2a)
- Determine health status of woman (2b)
- Assess the fetal wellbeing (2c)
- Monitor the progression of pregnancy (2d)
- Promote and support health behaviors that improve their wellbeing (2e)
- Provide anticipatory guidance related to pregnancy, birth, breastfeeding, parenthood, and change in the family (2f)
- Detect, manage, and refer women with complicated pregnancies (2g)
- Assist the woman and her family to plan for an appropriate place of birth (2h)
- Promote physiologic labour and birth (3a)
- Manage a safe spontaneous vaginal birth and prevent complications (3b)
- Provide care of the newborn immediately after birth (3c)
- Provide postnatal care for the healthy woman (4a)
- Provide care to healthy newborn infant (4b)
- Promote and support breast feeding (4c)
1. Basic sciences applied to midwifery
Theory: T-40 hours, Skill Lab: SL-12 hours, Clinical: CL-210 hours
A. Maternal, Fetal and Newborn Physiology
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-3 SL-4 |
|
Review of anatomy & physiology of human reproductive system
|
|
| Essay, short answers and MCQ |
2 | T-4 SL-2 |
|
Embryology and Fetal growth and development
|
| Foetal circulation – schematic representation | Evaluation of the assignment |
3 |
|
Physiological changes in pregnancy
|
|
|
B. Pharmacology and Diagnostics
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-3 |
| Review of Pharmacology
|
| Quiz | |
2 | T-3 |
| Medicines in pregnancy and breastfeeding
|
| Quiz | |
| 3 | T-4 |
| Commonly used medicines and their side effects
|
| Drug presentati on & Case reports |
|
| 4 | T-10 CL-90 |
| Prescription and safe administration of medicine
|
|
|
|
| 5 | T-3 CL-40 |
| Non Pharmacological Therapy: Complementary therapies and supplementation
|
| Demonst ration of various complimentary therapies during labor |
|
| 6 | T- 3 SL-2 CL-40 |
|
|
|
|
C. Infection Control
| 1 | T-4 SL-2 CL-40 | Infection Control |
| Infection Control
|
|
| OSCE /OSP E |
2. Normal Pregnancy, Birth and Puerperium
Theory: T-50 hours, Skill Lab: 22 hours, Clinical: CL- 680 hours
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-4 CL-40 |
| Chain of Referral system |
|
| Essay, short answers and MCQ |
2 | T-4 SL-2 |
|
Beginning the pregnancy journey
|
|
|
|
| 3 | T-6 SL-2 CL-50 |
|
Pregnancy assessment and midwifery care during 1st Trimester
|
|
|
|
| 4 | T-5 SL-2 CL-45 |
|
Midwifery care during 2nd trimester of pregnancy
|
|
|
|
| 5 | T-5 SL-3 CL-50 |
|
Midwifery care during 3rd trimester of pregnancy
|
|
|
|
| 6 | T-5 SL-2 CL-120 |
|
Midwifery care during first stage of labour Review of
|
|
|
|
| 7 | T-5 SL-2 CL-120 |
|
|
| Clinical scenarios |
|
| 8 | T-5 SL-2 CL-100 | Assessment and care of the newborn immediately following birth. |
Midwifery care during 3rd Stage of labour
|
|
|
|
| 9 | T-3 SL-3 CL-20 |
|
Midwifery care during 4th Stage of labour
|
|
| |
| 10 | T-8 SL-4 CL-135 |
|
Postpartum care/ Ongoing midwifery care of women Review of
|
|
|
|
3. Care of Newborn
Theory: T-10 hours, Skill Lab: SL- 6 hours, Clinical: CL- 90 hours
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-2 |
|
Family centered care
|
| Group discussion on family centered midwifery care | Essay, short answers |
2 | T-2 SL-4 CL-30 |
|
Ongoing care of newborns
|
|
|
|
3 | T-3 CL-30 |
|
Risk identification and referral
|
| Case study | |
4 | T-2 SL-2 CL-20 |
|
Nutritional needs of the newborn and establishing breastfeeding
|
|
| |
5 | T-1 CL-10 |
|
Immunization
|
| Case scenario – midwife ‘s role in immunization | Demonstra te skill in immunizat ion of the newborn. |
COURSE MODULE III: COMPLEX CARE OF WOMAN AND CARE OF COMPROMISED NEWBORN
Theory: 40 hours
Practicum: Skill lab: SL-35 hours | Clinical: CL- 570 hours
Course aim
This course will prepare the student to provide skilled, knowledgeable, compassionate and respectful midwifery care across the continuum of childbirth for mothers facing deviation from normalcy, in both community and institution. This course will examine the physiological impact of pre-existing health challenges and medical disorders experienced during pregnancy as well as pathophysiological response to deviations from normal and complications in the woman, fetus and newborn.
Course Description
This course will build on the knowledge obtained from the previous courses and will examine the pathophysiological impact of nutritional deficiencies, pre-existing medical disorders and existing disease burden in India as well as pathophysiological response to deviations from normal; including hypertensive, endocrine, haematological, haemorrhagic, metabolic disorders and obstetric emergencies. This module is designed to enable the NPMs to develop skills in identifying women with deviations from normal during the antenatal, intranatal and postnatal period and abnormal newborns and provide specialized care for them. The NPMs would be able to implement the national health programs with special reference to family welfare and women’s health. The module consists of
Perinatal Psychological Health, Complex care of woman and care of compromised newborn.
Course Objectives:
- Assess and provide care for women in the antenatal, intranatal and postnatal period facing complications
- Assess and provide care for neonates with problems
- Identify deviations from normalcy, stabilize and transport women and neonates to the higher centers
- Explain how common pre-existing health challenges interact with the physiological changes during pregnancy to increase the risk of complications.
- Explain the pathophysiological responses that occurs in the woman, fetus and newborn in response to deviations from normal and obstetric emergencies
- Understand the pathophysiology underlying common fetal and neonatal disorders, complications and congenital abnormalities
- Recognize and assess deviations from normal physiology during pregnancy, labour and birth and the puerperium
- Plan and provide evidence-based and compassionate, woman-centred midwifery care for women experiencing complications during the antenatal, intrapartum and postpartum period.
- Demonstrate effective clinical skills and appropriate use of technology in the care of women with complications and/or obstetric emergency
- Understand the impact of complications on the psychological, social and cultural wellbeing of women and their families and the importance of continuity of care.
- Describe the legal responsibilities associated with complications during the antenatal, intrapartum and postpartum period
- Identify the need for referral and interprofessional collaboration in managing the care of women with complex needs.
- Recognize woman who experiences physical and sexual violence and partner abuse and provide appropriate support and referral
- Promote health of families and communities and provide family welfare services
Competencies (ICM)
- Assess the health status, screen for health risks, and promote general health and well-being of women and infants(1j)
- Prevent and treat common health problems related to reproduction and early life(1k)
- Recognize conditions outside midwifery scope of practice and refer appropriately(1l)
- Detect, manage, and refer women with complicated pregnancies (2g)
- Provide care to women with unintended or mistimed pregnancy (2i)
- Detect and treat or refer postnatal complications in woman(4d)
- Detect and manage health problems in newborn infant ( 4e)
- Care for women who experience physical and sexual violence and abuse (1m)
- Provide family planning services (4f)
1. Perinatal Psychological Health
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-2 CL-20 |
|
Perinatal mental health disorders
|
| Online resources on perinatal mental health |
|
2 | T- 1 CL-20 |
|
Perinatal death, trauma and grief
|
| Journal clubperinatal mental health | MCQ, Short answers, Essays |
3 | T-1 CL-20 |
|
Perinatal wellbeing
|
| Group workScenario based learning |
|
1. Complex care of the woman
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T – 2 |
|
|
| Clinical scenarios – Women with complications | MCQ, Short answers , Essays |
2 | T – 2 CL -30 | Assess women with miscarriage and provide post abortion care |
|
|
| Assessment of clinical performance with rating scale |
3 | T – 5 SL – 5 CL -60 |
|
Recognition and Management of problems during Pre-pregnancy and Pregnancy
|
|
|
|
4 | T-5 SL-5 CL100 |
|
Complex care in labour
|
|
|
|
5 | T – 4 SL – 4 CL -30 |
|
Complex care during birth
|
|
|
|
6 | T – 3 SL – 2 CL -30 |
|
Interventions during complicated birth Forceps delivery
vacuum extraction
Caesarean section
Episiotomy, perineal and cervical lacerations; suturing
|
|
|
|
7 | T-1 SL-2 CL-30 |
|
Complex care during the third stage of labour
|
|
|
|
8 | T-2 CL-50 |
|
Complex care during the puerperium (Recognition and Management of postnatal problems)
|
|
|
|
9 | T – 1 SL – 2 | Demonstrate knowledge and ability to manage basic life -saving skills and adult CPR |
Resuscitation of the woman |
| OSCE |
1. Care of the Compromised Newborn
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-1 SL2 |
|
Context of neonatal care in India and the approach of different models of newborn care
|
|
| |
2 | T-2 SL2 |
|
Care of Compromised neonate during birth Needs of pre-term and low birth weight infants
Complications at birth affecting the neonate
|
|
|
|
3 | T-1 CL20 |
|
Compromised newborn with infection
|
|
|
|
4 | T-1 CL20 |
|
Compromised newborn with metabolic disorder Metabolic disorders
|
|
| |
5 | T-1 SL2 CL20 |
|
Compromised newborn with abnormal condition Abnormal conditions of the newborn
|
|
| |
6 | T-1 SL2 CL40 |
|
Global public health action in neonatal and childhood care Integrated management of neonatal childhood illness (IMNCI) Three components:
|
| Group work Clinical condition and management as per IMNCI |
|
7 | T-1 SL2 CL30 |
|
Feeding in compromised newborn Feeding problems of the newborn
|
| Demonstrate competencies in feeding compromised newborn |
|
1. Healthy families and Communities
Unit | Hours | Learning outcomes | Content | Teaching Learning activities | Assignments | Methods of Assessment |
1 | T-1 SL-2 |
|
Public Health approach: Information, Education and Communication (IEC)
|
| Role play SBCC | Develop a public health action and implement that includes SBCC |
2 | T-1 SL-3 CL30 |
|
Family planning
|
|
| |
3 | T-1 CL20 |
|
Gender related issues in SRHR
|
| Group workSituation analysis of women in the society and obstetric violence |
|
1. ANNEXURES
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE NPMs
The unique and major role of NPMs is promoting the health of women and childbearing families. The NPMs
- Work with women to promote self-careand the health of women, infants and families
- Respect and treat women with human dignity and as persons accorded full human rights
- View pregnancy as a normal physiologic life event
- Monitor the physical, psychological, spiritual and social well-being of the woman and her immediate family throughout the childbearing cycle
- Provide the woman with personal culturally appropriate advice, education, counselling, support and antenatal care
- Provide respectful maternity care
- Render continuity of care to women from pre pregnancy, antenatal, during labour, childbirth and immediately postpartum and ongoing support during the postnatal period
- Establish rapport in order to develop self-confidence in the woman to give birth and adapt to her new family dynamic
- Minimise unnecessary technological interventions during childbirth
- Identify the onset of complications, give emergency care and refer women and or newborns who require obstetrical or other specialist attention
- Focus on health promotion and disease prevention throughout the child bearing cycle.
ANNEXURE –II
CLINICAL LOGBOOK FOR NPM (PROCEDURAL COMPETENCIES/ SKILLS)
S.N | Specific procedural competencies/skills | Performs independently/Performs collaboratively with doctor/ Assists doctor in procedures (P/PC/A)* | Date & signature of the faculty |
1 | ANTENATAL CARE | ||
1.1 | Health assessment of antenatal woman: History taking, Physical examination and obstetrical examination | P | |
1.2 | Urine pregnancy test | P | |
1.3 | Estimation of hemoglobin using sahli’s hemoglobinometer /true Hb-P | P | |
1.4 | Preparation of peripheral smear for malaria | P | |
1.5 | Urine testing for albumin and sugar | P | |
1.6 | Point of care HIV test | P | |
1.7 | Point of care syphilis test | P | |
1.8 | Preparation of mother for USG | P | |
1.9 | Perform USG | PC | |
1.10 | Kick chart / DFMC (daily fetal movement count) | P | |
1.11 | Preparation and recording of CTG / NST/ CST | P | |
1.12 | Preparation/Assisting woman for antenatal investigationsamniocentesis, cordocentesis, Chorionic villus sampling | A | |
1.13 | Antenatal counseling- diet & exercise | P | |
1.14 | Administration of TT/Td-P | P | |
1.15 | Prescription of iron and folic acid tablets | ||
1.16 | Prenatal counseling and care of general and vulnerable groups such as adolescent pregnant mothers | P | |
2 | INTRANATAL CARE | ||
2.1 | Identification, assessment and admission of woman in labour | P | |
2.2 | Perform CTG | PC | |
2.3 | Vaginal examination during labour including Clinical pelvimetry | P | |
2.4 | Plotting and interpretation of partograph | P | |
2.5 | Preparation for delivery – physical and psychological | P | |
2.6 | Setting up of the delivery room / unit | P | |
2.7 | Pain management during labour-non-pharmacological | P | |
2.8 | Conduction of normal delivery | P | |
2.9 | Episiotomy only if required and repair | P | |
2.10 | Essential newborn care | P | |
2.11 | Active management of third stage of labour | P | |
2.12 | Examination of placenta | P | |
2.13 | Care during fourth stage of labour | P | |
2.14 | Initiation of breast feeding and lactation management | P | |
2.15 | Assessment and weighing of newborn | P | |
2.16 | Administration of Vitamin K | P | |
3 | POSTNATAL CARE | ||
3.1 | Postnatal assessment and care | P | |
3.2 | Perineal / episiotomy care | P | |
3.3 | Breast care | P | |
3.4 | Postnatal counseling-diet, exercise & breast feeding | P | |
3.5 | Postpartum family planning | P | |
4 | NEWBORN CARE | ||
4.1 | Assessment of newborn including gestational age | P | |
4.2 | Baby bath | P | |
4.3 | Kangaroo Mother Care | P | |
4.4 | Identification of minor disorders of newborn and their management | P | |
4. 5 | Neonatal immunization- Administration of BCG, Hepatitis B vaccine-P | P | |
5 | CARE OF WOMAN WITH COMPLICATIONS/HIGH RISK MOTHER | ||
5.1 | Identification of antenatal complications- pre- eclampsia, anemia, Antepartum hemorrhage | P | |
5.2 | Glucose challenge test / Glucose Tolerance test | P | |
5.3 | Administration of MgSo4 | P | |
5.4 | Identification of fetal distress and its management | P | |
5.5 | Preparation of woman for emergency / elective caesarean section and assisting in caesarean | A | |
5.6 | Prepare the mother and perform vacuum delivery when favourable | P | |
5.7 | Vacuum delivery | PC | |
5.8 | Diagnosis of malpresentations and malpositions | P | |
5.9 | Diagnosis and management of cord presentation/cord prolapse | P & PC | |
5.10 | Early diagnosis of preterm labor | P | |
5.11 | Prepare assess suitability for and conduct breech delivery when favorable | P | |
5.12 | Breech delivery | PC | |
5.13 | Infection prevention during labor and newborn care | P | |
5.14 | Diagnosis and management of prolonged labour | P | |
5.15 | Prepare and perform low forceps operation | P | |
5.16 | Forceps operation | A | |
5.17 | Manual removal of the placenta | PC | |
5.18 | Diagnosis and initial management of PPH- Bimanual compression of uterus, Balloon tamponade for atonic uterus, Aortic compression for PPH, Application of anti-shock garment, prescription and administration of fluids and electrolytes through intravenous | P & PC | |
5.19 | Repair of perineal and vaginal tears (upto II degree) | P | |
5.20 | Repair of perineal and vaginal tears (above II degree) | PC | |
5.21 | Identification and first aid management of obstetric shock | P | |
5.22 | Manage obstetric shock | PC | |
5.23 | Diagnosis and management of puerperal sepsis | P & PC | |
5.24 | Management of breast engorgement | P | |
5.25 | Management of thrombophlebitis | P & PC | |
6 | HIGH RISK NEWBORN | ||
6.1 | Identification of highrisk newborn | P | |
6.2 | Neonatal resuscitation | P | |
6.3 | Assisting in neonatal diagnostic procedures | A | |
6.4 | Feeding of high risk newborn –EBM(spoon/paladai) | P | |
6.5 | Insertion/removal/ feeding – Naso/oro gastric tube | P | |
6.6 | Administration of medication – oral / parenteral | PC | |
6.7 | Neonatal drug calculation | P | |
6.8 | Oxygen administration | P | |
6.9 | Care of neonate in incubator / warmer/ventilator | P | |
6.10 | Neonatal intubation / ventilator | PC | |
6.11 | Care of neonate on phototherapy | P | |
6.12 | Assist in exchange transfusion | A | |
6.13 | Organizes different levels of neonatal care | P | |
6.14 | Transportation of high risk newborn | P | |
7 | FAMILY WELFARE | ||
7.1 | Family planning counseling | P | |
7.2 | Distribution of temporary contraceptives – condoms, OCP’s, emergency contraception | P | |
7.3 | Insertion and removal of Interval IUCD | P | |
7.4 | Insertion and removal of PPIUCD/PAIUCD | P | |
7.5 | Preparation of the woman for Postpartum sterilization | P | |
7.6 | Prepare and assist in tubectomy | A | |
8 | OTHER PROCEDURES | ||
8.1 | Prepare and assist for D&C / D&E operations | A | |
8.2 | Perform Manual Vacuum Aspiration | P & PC | |
8.3 | Post abortion care | P | |
8.4 | Post abortion family planning services | P | |
8.5 | Post abortion counseling | P | |
8.6 | Pre-conception nutritional assessment, screening HIV,Cervical cancer | P | |
8.7 | Preconception counseling and care | P | |
8.8 | Pap smear | P | |
8.9 | Visual inspection with acetic acid / iodine | P | |
8.10 | Counseling on breast self-examination | P | |
8.11 | Conduction of maternal and perinatal death audit | PC | |
8.12 | Maintenance of registers | P | |
8.13 | Maintenance of records | P | |
* When the learner is found competent to perform the skill, the faculty/trainer will sign it.
Learners: are expected to perform the listed skills/competencies many times until they reach level 3 competency,
after which the faculty signs against each competency.
Faculty/Trainers: Must ensure that the signature is given for each competency only after they reach level 3.
- Level 3: competency denotes that the leaner is able to perform that competency without supervision
- Level 2: Competency denotes that the learner is able to perform each competency with supervision
- Level 1 :competency denotes that the learner is not able to perform that competency/skill even with supervision
ANNEXURE-III
CLINICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR NPM PROGRAM
S.N. | Clinical requirement | Date | Signature of the Faculty/Preceptor |
1 | Antenatal assessment and care- 70 | ||
2 | Postnatal assessment and care– 70 | ||
3 | Assessment of labour using partograph – 40 | ||
4 | Per vaginal examination if required – 20 | ||
5 | Witnessing Conduction of birth – 10 | ||
6 | Conduction of delivery (independent)–40 | ||
7 | Assisting conduction of abnormal/assisted delivery – 15 | ||
8 | Placental examination-10 | ||
9 | Episiotomy and suturing if indicated – 10 | ||
10 | Insertion of Interval IUCD – 5 | ||
11 | Insertion of PPIUCD /PPIUCD– 5 | ||
12 | Newborn assessment – 25 | ||
13 | ENBC-25 | ||
14 | Newborn Resuscitation – 5 | ||
15 | Kangaroo Mother care – 5 | ||
16 | Antenatal care study – 1 Diagnosis: | ||
17 | Postnatal care study- 1 Diagnosis: | ||
18 | Newborn care study- 1 Diagnosis: | ||
19 | Clinical presentation – 4
| ||
20 |
Health talk
| ||
21 | Counseling mothers &family members 1. 2. | ||
22 | Bed side clinics – 2 1. 2. | ||
23 | Clinical Seminar/ Clinical Conference Topic: | ||
24 | Drug study, presentation and report – 1 Drug: | ||
25 | Visits –report Peripheral health facility | ||
26 | Project/ Journal Club: Evidence based midwifery practice (Individual/Group ) -1 Topic: | ||
27 | Continuity of Care experiences 15 |
Signature of the Program coordinator
ANNEXURE-IV
CLINICAL EXPERIENCE DETAILS FOR NPM PROGRAM
Area of posting | Clinical Condition | Number of days care given | Signature of Faculty/Preceptor |
Signature of the Program coordinator
ANNEXURE V
LEARNING RESOURCES
GOI Guidelines (MNH)
- LaQshya- Labour Room Quality Improvement Initiative Guideline
- Guidelines for standardization of labour rooms at delivery point
- Dakshata: Empowering Providers for Improved MNH Care during Institutional Deliveries
- SBA-Guidelines for Antenatal Care and Skilled Attendance at Birth by ANMs/LHVs/SNs ,Hand book and trainers Guide
- IMNCI training modules,photo and chart booklets
- NavjatShishu Suraksha Karyakram guidelines
- Routine Immunization Handbook for Health Workers
- Postpartum FP handbook for Service Providers
- IUCD reference manual for medical officers and nursing personnel
- PPIUCD reference manual
- Operational guidelines: Introduction of Haemophilus influenza b (Hib) as Pentavalent Vaccine in Universal Immunization Program of India
- Use of antenatal corticosteroids in preterm Labour
- Facility based IMNCI(F-IMNCI)(Participants manual and Chart booklet)
- Guidance note on use of Uterotonics during labour
- Vitamin K prophylaxis at birth(in facilities)
- National guideline for calcium supplementation during pregnancy
- National guideline on management of Hypothyroidism duringPregnancy
- National Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Screening for Syphilis during pregnancy
- National guidelines Respectful newborn care-Child Health Division, MoHFW
- Guidance for Mentoring and support visit-DAKSHATA
- Guideline on midwifery services in India-2018
Other resources
- WHO Report on Strengthening quality midwifery care and midwifery education
- The Lancet Series 2014, 2018 – Midwifery Quality Maternal and Newborn Care (QMNC) Framework
- ICM Essential Competencies for midwifery Practice (2019)
- WHO midwifery educator competencies
- Safe delivery app
ANNEXURE VI
ICM STATEMENT ON MIDWIFERY AND MODEL OF CARE
Midwifery care is provided by an autonomous midwife in collaboration with the maternity care team. Midwifery
competencies (knowledge, skills and attitudes) are held and practised by midwives, educated through a pre-service/preregistration midwifery education programme that meets the ICM global standards for midwifery education.
The ICM’s definition of midwifery reflects its core statement of philosophy and model of care the key points of
which follow.
- Pregnancy and childbearing are usually normal physiological processes
- Pregnancy and childbearing is a profound experience, which carries significant meaning to the woman, her family, and the community.
- Midwives are the most appropriate care providers to attend childbearing women.
- Midwifery care promotes, protects and supports women’s human, reproductive and sexual health and rights, and respects ethnic and cultural diversity.
- It is based on the ethical principles of justice, equity, and respect for human dignity.
- Midwifery care is holistic and continuous in nature, grounded in an understanding of the social, emotional, cultural, spiritual, psychological and physical experiences of women.
- Midwifery care is emancipatory as it protects and enhances the health and social status of women, and builds women’s self confidence in their ability to cope with childbirth
- Midwifery care takes place in partnership with women, recognising the right to self-determination, and is respectful, personalised, continuous and non-authoritarian.
- Ethical and competent midwifery care is informed and guided by formal and continuous education, scientific research and application of evidence.
ICM Model of Midwifery Care (ICM 2014).
- Midwives promote and protect women’s and newborns’ health and rights.
- Midwives respect and have confidence in women and in their capabilities in childbirth.
- Midwives promote and advocate for non-intervention in normal childbirth.
- Midwives provide women with appropriate information and advice in a way that promotes participation and enhances informed decision-making.
- Midwives offer respectful, anticipatory and flexible care, which encompasses the needs of the woman, her newborn, family and community, and begins with primary attention to the nature of the relationship between the woman seeking midwifery care and the midwife.
- Midwives empower women to assume responsibility for their health and for the health of their families.
- Midwives practice in collaboration and consultation with other health professionals to serve the needs of the woman, her newborn, family and community.
- Midwives maintain their competence and ensure their practice is evidence-based.
- Midwives use technology appropriately and effect referral in a timely manner when problems arise.
- Midwives are individually and collectively responsible for the development of midwifery care, educating the new generation of midwives and colleagues in the concept of lifelong learning.
ANNEXURE VI
REFERENCES
- Government of India (2018) Guidelines on Midwifery Services in India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India and National Health Mission, India
- Miller S, Abalos E, Chamillard M, Ciapponi A, Colaci D, Comandé D, Diaz V, Geller S, Hanson C, Langer A, Manuelli V, Millar K, Morhason-Bello I, Castro CP, Pileggi, VN, Robinson N, Skaer M, Souza, JP, Vogel, JP & Althabe, F (2016). ‘Beyond too little, too late and too much, too soon: a pathway towards evidence-based, respectful maternity care worldwide.’ The Lancet, 388(10056): 2176-2192.
- Sandall J, Soltani H, Gates S, Shennan A, Devane D. Midwife-led continuity models versus other models of care for childbearing women. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD004667. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004667.pub5
- ICM 2013 International Confederation of Midwives Global Standards for Midwifery Education (2013) accessed August 2019 at https://www.internationalmidwives.org/assets/files/general-files/2018/04/icm-standardsguidelines_ammended2013.pdf
- ICM Essential Competency Standards for the Midwife (ICM 2018) accessed on July 12-7-19 at https://www.internationalmidwives.org/our-work/policy-and-practice/essential-competencies-for-midwiferypractice.html
- Renfrew M, McFadden A, Bastos M, Campbell J et al. (2014) Midwifery and quality care: findings from a new evidence informed framework for maternal and newborn care. Lancet 384; 1129-1145
- WHO (2019) Strengthening Quality Midwifery Education Framework for Action, Universal health Coverage 2030, World health Organisation, Geneva
- International Confederation of Midwifery accessed August 2019 at https://www.internationalmidwives.org/
- Every woman Every Child The Global Strategy for Women’s Children’s and Adolescents 2016-2030 (2015) access 14th July 2019 at https://www.who.int/life-course/partners/global-strategy/ewec-globalstrategyreport200915.pdf?ua=1
- Chorazy M and Klinedinst K (2019) Learning by doing: A model for incorporating high-impact experiential learning into an undergraduate public health curriculum > Frontiers in Public Health Journal 7(31):1-6 access 14th July 2019 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00031/full
- Kolb DA. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall (1984).
- Dewey J. Experience and Education. New York, NY: Collier Books (1938).
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2012 Antenatal Care, Quality Statement 2 Services – continuity of care. NICE, UK. Viewed online August 2016 https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/qs22/chapter/quality-statement-2- services-continuity-of-care
- Australian Nursing and Midwifery Accreditation Council (ANMAC) 2014 Midwife accreditation standards, ANMAC, Canberra accessed July 15th 2019 at https://www.anmac.org.au/sites/default/files/documents/ANMAC_Midwife_Accreditation_Standards_2014.pdf
- Midwifery Council of New Zealand (2015) Standards for approval of pre-registration midwifery education programmemes and accreditation of tertiary education organisations (2nd edition) July 2015 Wellington, New Zealand accessed August 2019 athttps://www.midwiferycouncil.health.nz/sites/default/files/professionalstandards/Midwifery_Standards_2015_web_final.pdf
- Nursing and Midwifery Council 2009 Standards for pre-registration midwifery education. London UK accessed August 2019 at https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/standards/nmc-standards-for-preregistrationmidwifery-education.pdf
- Smith M, Warnes S and Vanhoestenberghe A 2018 Scenario-based learning in Teaching and Learning in Higher Education: Perspectives from UCL, Ch. 10 Ed Davies, J and Pachler N. UCL Institute of Education Press, University College, London.
- Gibbs G (1988) Learning by Doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit. Oxford Polytechnic: Oxford
- WHO (2015) Improving the Quality of care for Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child and Adolescent Health in South-East Asia. World health Organisation. South East Asia
- Cooper, S, Cant, R. Porter, J Bogossian F,Mckenna L Brady, S and Fox-Yound S 2012 . Simulation based learning in midwifery education: A systematic review. Women and Birth, Volume 25, Issue 2, 64 – 78
- Coffey, F., 2015, Learning by simulation – is it a useful tool for midwifery education? New Zealand College of= Midwives Journal Issue 51 30-36
- Finlay, L. (2008). Reflecting on ‘Reflective practice’. 1st ed. [ebook] The Open University. Available at: http://www.open.ac.uk/opencetl/files/opencetl/file/ecms/web-content/Finlay-(2008)-Reflecting-on-reflectivepractice-PBPL-paper-52.pdf [Accessed July 12th 2019]


![Indian Nursing Council [Nurse Practitioner in Midwifery (NPM) Program], Regulations, 2020](https://news.collegeadmission.co/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/indian-nursing-council-nurse-practitioner-in-midwifery-npm-program-regulations-2020.jpeg)
